Water purifiers are essential kitchen tools for every household today and understanding how water purifiers work can uncover the dynamics for choosing the right water purifier.

Various models sell in the markets, and choosing the best one requires a thorough knowledge of various water purification technologies, working procedures of water purifiers, their use, and factors governing the performance of water purifiers. Let us start with the water purification technologies first, and we will see how the various water purification technologies are interrelated to serve the diverse water purification needs.
The later part of this article will deal with explaining how water purifiers work, and how you should maintain them.
Let’s start!
Various Water Purification technologies
Water quality, especially in urban areas, is deteriorating with time. Even the rural areas are facing issues with the availability of pure drinking water. This has led to the development of water purification technologies that serve the varying water purification needs. What we have today, especially in metro cities, desperately needs aggressive purification methodologies to counter physical and biological impurities. The working of water purifiers employs various technologies such such as UF+UV+RO+Minerals to give the best purification results.
Let’s dive into understanding the various water purification technologies and learn which one suits your water treatment requirements. A thorough study will give insights into how water purifiers work.
UV Technology
The UV technology does not remove the dissolved solids or any other suspended impurities in water. It only kills the biological microorganisms in water or damages their DNA so that they do not replicate in our bodies if consumed. All the water purifiers presented in our list of the best water purifiers in India for home come embedded with UV technology.
The mastery of this technology is using ultraviolet radiation in the wavelength range of 198 nm to 400 nm. The UV rays pass through the water, where they encounter different germs and kill them or damage their DNA.
UF Technology
UF (Ultra Filtration) water purifiers purify the water by filtering it under gravity pressure, and hence no electricity is required. Thus, their initial cost is low compared to the rest technologies of water purification. These are the most suitable water purifiers when it comes to the place where there is no electricity, or the power cuts are frequent. These are the best non-electric water purifiers.
RO System
The Reverse osmosis system of water purification, abbreviated as RO system, employs passing the impure water (raw water) through a semi-permeable membrane (a polymeric membrane in most cases) under pressure to remove impurities as fine as 0.0001 to 0.001 microns. Yes, that’s the size of pores in RO membranes. These membranes have the finest pores available in water purification technologies thus far, empowering them to remove even the dissolved solids apart from the other colloidal particles and microorganisms.
As a next step to understanding how water purifiers work, let us move on to understanding the various components used in the water purifiers.
Components of Water Purifiers
The various water purification technologies led to the development of respective water purifiers, and some manufacturers, depending upon the initial water quality, clubbed the various technologies together to develop a sophisticated versions such as a water purifier with RO+VU+UF technology. Let us understand how water purifiers work with the perspective of components used in the water purifiers.
Pre Sediment Filter
The pre-sediment filter is the first membrane the raw water passes through. Designed to remove large particles, the pores of pre-sediment filters usually range between 5 to 25 microns, depending upon the make and quality of pre-sediment filter membranes.
Inline Sediment Filter
The inline sediment filter is the second largest poresbased membrane located after the pre-sediment filter. The pores of this filter membrane are usually 5 microns in size.
Activated Carbon Filter
The Activated carbon filters absorb organic compounds such as chlorine, and improve the taste and odour of the inlet water. Pores in activated charcoal are uniformly distributed and usually range between 1 to 25 nanometers in size
UF Filter
UF stands for Ultrafilteration and membranes of UF filter range between 0.1 to 0.01 microns in size. This layer is designed to remove all major components including microorganisms till 0.01 microns in size. This, however, doesn’t filter the dissolved solids.
Reverse Osmosis Membrane
The RO membranes are the finest in size with as small as 0.0001 microns in size. These membranes remove all impurities including the dissolved solids to a greater extent.
UV Lamp
The UV lamp emits ultraviolet radiation that kills the pathogens, and other microorganisms in the water.
Since we are done with understanding the various water purification technologies and the components of a water purifier, let’s move on to understanding how water purifiers work.
How Water Purifiers Work?
Every domestic water purifier works on the principle of removing impurities by filtering the water with the help of membranes and killing the microbiological organisms with Ultraviolet radiation. Though the manufacturers are also deploying some purifying agents and other technologies that add minerals to the purified water, these essentially may not be required every time. It all depends upon the source of water responsible for initial impurities and mineral contents in it.
The extent of impurities removal, post-membrane, depends on the size of the holes on the membrane’s layer. In some purification technologies, due to the removal of a significant quantity of total dissolved solids (TDS), the pH value of purified water falls towards the lower side of the desired limit range.
It means that the purified water becomes slightly acidic. As the experts suggest that we should drink alkaline water, modern water purifiers come with an additional cartridge that increases the TDS level & PH level to the desired range, making it alkaline.
Now let us understand the sequence of “how water purifiers work,” i.e. the water flow sequence and the purification technologies that it passes through.
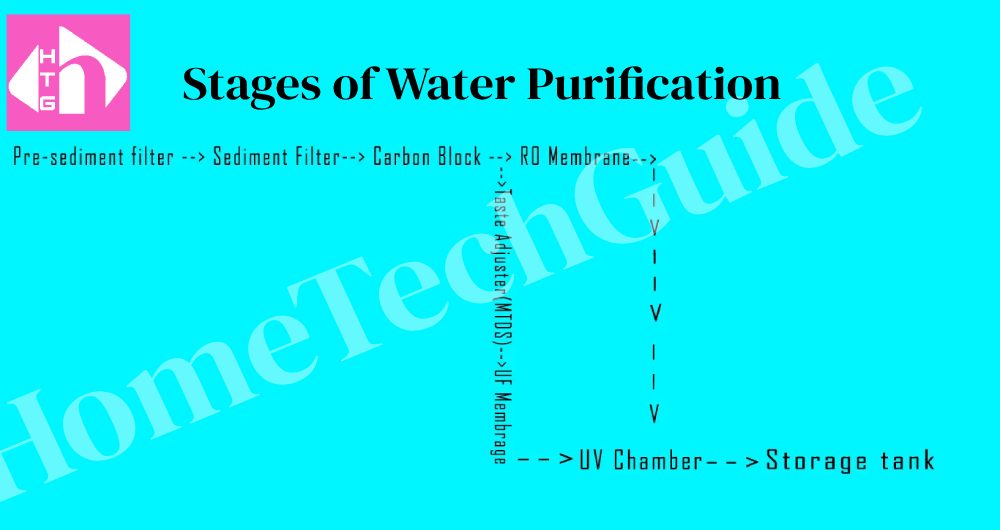
How water Purifiers Work – 7 Stages of Purification.
- The raw water (supply water) enters into the Pre-sediment filter, where it passes through a membrane with comparatively large holes and removes the solid particles in the water.
- In the next step, the water passes through the inline sediment filter with smaller holes than the one in the pre-sediment filter stage. The pores size in the sediment filter is, generally, 5 microns in size.
- In the third step, The water passes through carbon blocks (activated carbon). The carbon blocks are porous in structure and have excellent absorption properties. The pores in carbon blocks vary in size, usually from 1 nanometer to 25 nanometers, distributed un-uniformly throughout the carbon blocks. Macro impurities, along with the excess Chlorine in water get removed here. Since the chlorine quantity in water is tapped down here, the water improves in taste and odour.
- Now, in the fourth step, the water from the activated carbon chamber is sent in two directions
- One pumped towards the RO membrane, and
- Second, by gravity to the UF membrane
The flow of water towards UF is controlled by a TDS Controller/ TDS adjuster valve.
- Though both membranes can filter the microorganisms in the water, still, a UV chamber is still provided after these two purification membranes, which is in the 5th stage. The UV chamber kills pathogens, if any, in water. The pathogens may pass the filter membrane(RO and UF) if a rift occurs in the layer. There is a regulatory flow valve at the end of the UV chamber to reduce the flow rate inside the UV chamber, enabling the effective disinfection of germs in the water.
- The next step/ feature, found in some water purifiers, is the presence of an Alkaline cartridge.
The alkaline cartridge comes in water purifiers that use an RO membrane to filter the water when the TDS controlling technique is not used. OR when even after using a TDS control valve, more alkaline water is desired.
In this scenario, as 90% of TDS is filtered by the RO membrane, the pH of the outlet water shifts towards the low range of pH Level. (6.5 – 8.5 as recommended by BIS). This shift towards the lower side indicates the water is more acidic than alkaline. Though the water may remain under the limit, it is always advised by health experts to drink more alkaline water.
- In the 7th stage, the purified water gets collected in the storage tank. As soon as the storage tank gets filled, the float switch cuts the main supply and the solenoid valve closes, restricting the further supply of water in the sediment filter.
These are the 7 stages of purification explaining the working of water purifiers.
Benefits of Using a Water Purifier
- Provides access to clean, safe drinking water
- Removes harmful contaminants and impurities
- Improves the taste and odour of water
- Protects against waterborne diseases
Maintenance and Care Tips for Water Purifiers
- Regularly replace filters and cartridges as per the manufacturer’s recommendations
- Clean the purifier’s components periodically to prevent buildup of impurities
- Ensure proper installation and placement to optimize performance
- Schedule professional servicing to maintain efficiency and longevity
Conclusion:
The understanding of water purifiers workings can help you understand the dynamics of water purification and choose a technology that serves your family needs at the best. The above illustration on “How water purifiers work” is a general way that all water purifiers purify the raw water. There can be additional elements to it, that modern water purifiers are coming with. Like the mineral cartridge or the Copper cartridge, the additional elements may not be your requirement if you are using municipal water or water from a source that does not offer much contamination. Among the many imperatives, we should achieve the goal of drinking pure water with recommended mineral content.
FAQs
Is boiling water sufficient to make it safe for drinking?
Boiling kills the biological impurities in water but doesn’t account for TDS content or other impurities in water.
Do all water purifiers provide the same level of purification?
The extent of purification depends on the technology used in the water purifier, making the water filters offer different levels of filtration and purification.
Are water purifiers expensive and difficult to maintain?
The initial purchasing cost varies as per model and technology use. Maintaining the water requires replacing the filters which incur additional costs over 6 months or so, depending upon the inlet water quality. This may still be regarded as a value investment in health and well-being. This may still not prove costly as some companies offer free service and membrane replacement over a time duration.
Do water purifiers remove all contaminants from water?
While water purifiers are highly effective in removing many contaminants, it’s essential to choose the right type of purifier based on the specific impurities present in the water source.
